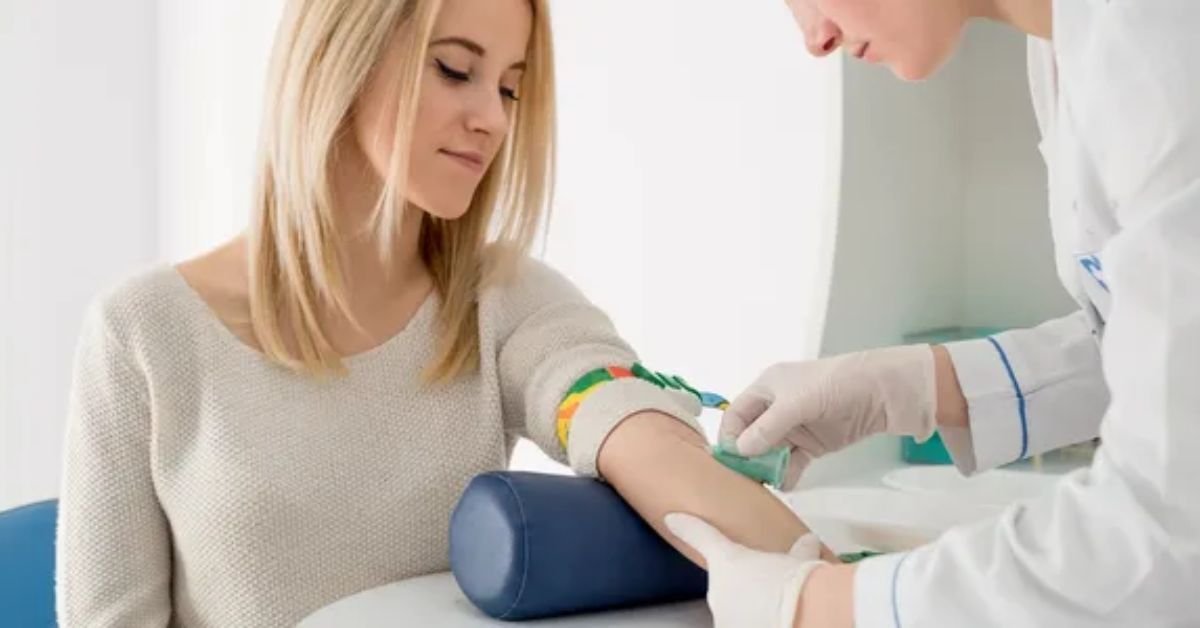
When it comes to identifying blood sugar problems early, the 2 Hour Diabetes Test is one of the most reliable diagnostic tools used worldwide. If you have ever been asked to drink a sweet solution at a lab and wait for blood to be taken two hours later, you have likely experienced the 2 Hour Diabetes Test. This test helps doctors understand how your body handles glucose over a fixed period of time.
The 2 Hour Diabetes Test is commonly used to diagnose type 2 diabetes, prediabetes, and gestational diabetes. Unlike a random blood sugar reading, the 2 Hour Diabetes Test shows how efficiently your body processes sugar after a controlled glucose load. It gives more insight than a single fasting test because it evaluates your metabolic response over time.
Many people feel anxious when they are told they need the 2 Hour Diabetes Test, especially during pregnancy or after abnormal fasting results. However, the 2 Hour Diabetes Test is simple, safe, and widely used. In this detailed guide, you will learn exactly what the 2 Hour Diabetes Test is, why it matters, how it works, who needs it, how to prepare, how results are interpreted, and what happens next.
Understanding the 2 Hour Diabetes Test
The 2 Hour Diabetes Test is formally known as the Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT). During the 2 Hour Diabetes Test, a person drinks a measured glucose solution, and blood samples are taken to measure how much sugar remains in the bloodstream after two hours.
The main purpose of the 2 Hour Diabetes Test is to evaluate how well insulin works. Insulin is the hormone that moves glucose from the blood into cells. If insulin is not working effectively, blood sugar levels remain high during the 2 Hour Diabetes Test.
The 2 Hour Diabetes Test is particularly helpful because some individuals have normal fasting glucose but abnormal post-meal glucose levels. In such cases, the 2 Hour Diabetes Test can detect early glucose intolerance before fasting tests show problems.
Why the 2 Hour Diabetes Test Is Important?
The 2 Hour Diabetes Test plays a critical role in early diagnosis. Diabetes often develops slowly. Many people feel perfectly fine while their blood sugar gradually increases. The 2 Hour Diabetes Test can detect changes before severe symptoms appear.
The 2 Hour Diabetes Test helps prevent complications. When high blood sugar remains untreated, it may damage the heart, kidneys, eyes, and nerves. Identifying abnormal results from the 2 Hour Diabetes Test allows early lifestyle changes or treatment.
Doctors also rely on the 2 Hour Diabetes Test during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes can affect both mother and baby. The 2 Hour Diabetes Test ensures timely detection and proper management.
Who Needs the 2 Hour Diabetes Test?
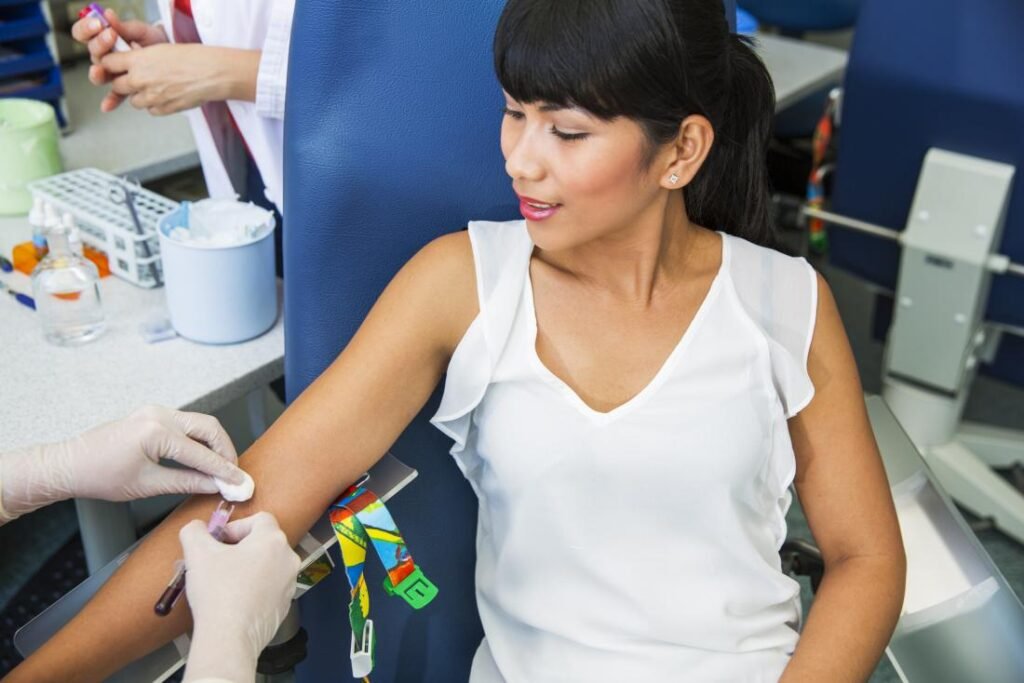
Not everyone requires the 2 Hour Diabetes Test. However, certain groups are more likely to be recommended for it.
1. People With Prediabetes Risk Factors
Individuals who are overweight, physically inactive, or have a strong family history of diabetes are often advised to take the 2 Hour Diabetes Test. High blood pressure, abnormal cholesterol, or a history of heart disease can also increase risk. The 2 Hour Diabetes Test helps detect early insulin resistance and impaired glucose tolerance before symptoms appear, allowing timely lifestyle changes and preventing progression to type 2 diabetes.
2. Pregnant Women
Pregnant women are commonly screened with the 2 Hour Diabetes Test between 24 and 28 weeks to detect gestational diabetes. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can reduce insulin effectiveness, raising blood sugar levels. The 2 Hour Diabetes Test ensures early diagnosis, protecting both mother and baby from complications such as high birth weight, premature delivery, and future diabetes risk, while supporting safe pregnancy management and healthy outcomes.
3. Individuals With Borderline Fasting Sugar
When fasting blood sugar levels are slightly elevated but not clearly diagnostic, doctors may recommend the 2 Hour Diabetes Test for further evaluation. This test measures how the body handles glucose after a controlled intake, providing clearer confirmation of prediabetes or diabetes. The 2 Hour Diabetes Test is especially useful when fasting results fall into the impaired range but symptoms remain absent.
4. People With Symptoms of Diabetes
People experiencing increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained fatigue, blurred vision, or slow wound healing may need the 2 Hour Diabetes Test. These symptoms often indicate elevated blood sugar levels. The 2 Hour Diabetes Test helps confirm whether diabetes is present by assessing the body’s glucose response over time, enabling early diagnosis and prompt treatment to prevent long-term health complications.
How the 2 Hour Diabetes Test Is Performed
Understanding each stage of the 2 Hour Diabetes Test can make the experience feel straightforward and manageable. The procedure is carefully structured to measure how your body processes glucose over a fixed period. The 2 Hour Diabetes Test typically takes slightly more than two hours from start to finish and is carried out in a laboratory or clinical setting under professional supervision.
1: Fasting
Before the 2 Hour Diabetes Test, you must fast for 8 to 12 hours to ensure accurate baseline results. During this fasting period, only plain water is allowed. Food, sugary drinks, tea, coffee, or smoking can interfere with the 2 Hour Diabetes Test results. Fasting allows healthcare providers to measure your true resting blood glucose level before introducing the glucose solution for testing.
2: Initial Blood Sample
At the beginning of the 2 Hour Diabetes Test, a healthcare professional draws a fasting blood sample. This first sample measures your baseline blood glucose level before consuming any sugar. The initial reading is essential because it provides a comparison point for the final result. The 2 Hour Diabetes Test relies on this baseline measurement to evaluate how much your blood sugar rises after glucose intake.
3: Drinking the Glucose Solution
After the first blood sample, you will be given a measured glucose drink, usually containing 75 grams of sugar for adults. The drink is sweet and must be consumed within a few minutes. This step is central to the 2 Hour Diabetes Test because it challenges your body’s insulin response. The controlled glucose amount ensures consistent and reliable results across different individuals undergoing testing.
4: Waiting Period
Once the glucose solution is consumed, the two-hour waiting period begins. During the 2 Hour Diabetes Test, you must remain seated and avoid eating, drinking anything except small amounts of water, or engaging in physical activity. Movement can alter glucose metabolism and affect accuracy. This resting phase allows your body to process the sugar naturally, ensuring the 2 Hour Diabetes Test reflects true metabolic function.
5: Final Blood Sample
Exactly two hours after drinking the glucose solution, a second blood sample is taken. This final measurement determines how much glucose remains in your bloodstream. The difference between the initial and final readings defines the outcome of the 2 Hour Diabetes Test. Once the second sample is collected, the 2 Hour Diabetes Test is complete, and results are usually available within a short period.
What Do the 2 Hour Diabetes Test Results Mean?
The results of the 2 Hour Diabetes Test are measured in milligrams per decilitre (mg/dL).
For non-pregnant adults:
- Less than 140 mg/dL: Normal
- 140 to 199 mg/dL: Prediabetes
- 200 mg/dL or higher: Diabetes
For pregnant women, slightly different thresholds apply in the 2 Hour Diabetes Test.
A result of 200 mg/dL or more during the 2 Hour Diabetes Test typically confirms diabetes, especially if symptoms are present.
The 2 Hour Diabetes Test During Pregnancy
The 2 Hour Diabetes Test is widely used to diagnose gestational diabetes. Pregnancy hormones can interfere with insulin function, making the 2 Hour Diabetes Test especially important.
If the 2 Hour Diabetes Test shows elevated glucose during pregnancy, doctors create a management plan that includes dietary changes, monitoring, and sometimes insulin therapy.
Most women return to normal glucose levels after delivery, but an abnormal 2 Hour Diabetes Test during pregnancy increases future diabetes risk.
How the 2 Hour Diabetes Test Compares to Other Tests
Several diagnostic tools are used to detect diabetes, and each serves a specific purpose. The 2 Hour Diabetes Test is widely recognised for evaluating how the body responds to a measured glucose load. While fasting blood sugar, HbA1c, and random blood sugar tests are useful, the 2 Hour Diabetes Test offers deeper insight into post-meal glucose handling and early insulin resistance.
1. Fasting Blood Sugar
The fasting blood sugar test measures glucose levels after at least eight hours without food. It provides a snapshot of baseline blood glucose but does not show how the body processes sugar after eating. Unlike the 2 Hour Diabetes Test, it cannot assess post-glucose response. The 2 Hour Diabetes Test is more comprehensive because it tracks how effectively insulin manages a controlled glucose challenge over time.
2. HbA1c Test
The HbA1c test measures the average blood sugar level over the previous two to three months by assessing glycated haemoglobin. It reflects long-term glucose exposure rather than immediate changes. In contrast, the 2 Hour Diabetes Test evaluates real-time glucose tolerance after sugar intake. While HbA1c is convenient and does not require fasting, the 2 Hour Diabetes Test can detect early abnormalities that average readings might miss.
3. Random Blood Sugar
A random blood sugar test measures glucose at any time of day without preparation. It is often used when symptoms are present. However, it lacks the structured design of the 2 Hour Diabetes Test. Because the 2 Hour Diabetes Test uses a standardised glucose load and timed measurements, it provides more controlled and reliable data for diagnosing impaired glucose tolerance and early diabetes.
Preparing Properly for the 2 Hour Diabetes Test
Proper preparation ensures accurate results from the 2 Hour Diabetes Test.
- Eat normally for three days before the test
- Avoid extreme dieting
- Inform your doctor about medications
- Get adequate sleep
- Do not smoke before the 2 Hour Diabetes Test
Failure to follow instructions may alter 2 Hour Diabetes Test outcomes.
What Can Affect the 2 Hour Diabetes Test Results?

Several factors can influence the 2 Hour Diabetes Test:
- Stress
- Illness
- Certain medications
- Physical inactivity
- Dehydration
Doctors consider these factors when interpreting the 2 Hour Diabetes Test.
Risks and Side Effects
The 2 Hour Diabetes Test is safe. Some people may feel:
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Sweating
- Fatigue
These symptoms usually resolve quickly after the 2 Hour Diabetes Test is completed.
What Happens After the 2 Hour Diabetes Test?
If your 2 Hour Diabetes Test result is normal, you may simply continue routine health monitoring.
If the 2 Hour Diabetes Test indicates prediabetes, lifestyle changes such as diet improvement and exercise are recommended.
If the 2 Hour Diabetes Test confirms diabetes, your doctor will discuss medication, monitoring, and long-term care.
Lifestyle Changes After an Abnormal
An abnormal 2 Hour Diabetes Test does not mean immediate complications. It is a warning sign.
Healthy changes include:
- Balanced meals
- Regular physical activity
- Weight management
- Reduced sugar intake
- Regular follow-up testing
Early intervention after the 2 Hour Diabetes Test significantly reduces long-term risks.
Long-Term Importance of the 2 Hour Diabetes Test
The 2 Hour Diabetes Test is not just a diagnostic tool. It is a preventive measure. By identifying abnormal glucose tolerance early, the 2 Hour Diabetes Test supports long-term health planning.
Many individuals diagnosed early through the 2 Hour Diabetes Test successfully control their blood sugar without severe complications.
Must Read:
- Which is the Best Blood Sugar Testing Machine?
- New Developments in Diabetes Treatment
- What Are the Top 10 Diabetes Medications?
FAQs:
1. Is the 2 Hour Diabetes Test painful?
The 2 Hour Diabetes Test involves two blood draws, which may cause minor discomfort.
2. Can I drink water during the 2 Hour Diabetes Test?
Yes, small amounts of water are allowed during the 2 Hour Diabetes Test.
3. How long does the 2 Hour Diabetes Test take?
The 2 Hour Diabetes Test takes slightly over two hours from start to finish.
4. Is the 2 Hour Diabetes Test accurate?
The 2 Hour Diabetes Test is considered highly accurate when properly conducted.
5. Do I need the 2 Hour Diabetes Test every year?
It depends on your risk factors and previous results.
6. What if I fail the 2 Hour Diabetes Test?
Your doctor will discuss next steps, which may include repeat testing or treatment.
Final Thoughts:
The 2 Hour Diabetes Test remains one of the most effective ways to diagnose diabetes and prediabetes early. It provides valuable information about how your body processes sugar over time, which a simple fasting test cannot fully reveal.
If your doctor recommends the 2 Hour Diabetes Test, consider it an opportunity. Early detection leads to better management and fewer complications. With modern medicine and proper lifestyle adjustments, even an abnormal 2 Hour Diabetes Test result can be managed successfully.
Your health is shaped by awareness and action. The 2 Hour Diabetes Test is not something to fear. It is a practical step toward understanding your body and protecting your long-term wellbeing.
If you are at risk or experiencing symptoms, speak with your healthcare provider about whether the 2 Hour Diabetes Test is right for you.